MIT OpenCourseWare
MIT 8.821 String Theory and Holographic Duality, Fall 2014
View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/8-821F14
Instructor: Hong Liu
In this lecture, Prof. Liu gives a physical interpretation of the black hole temperature, and similarly the temperature experienced by an accelerated observer in Minkowski spacetime.
License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA
More information at http://ocw.mit.edu/terms
More courses at http://ocw.mit.edu
Source
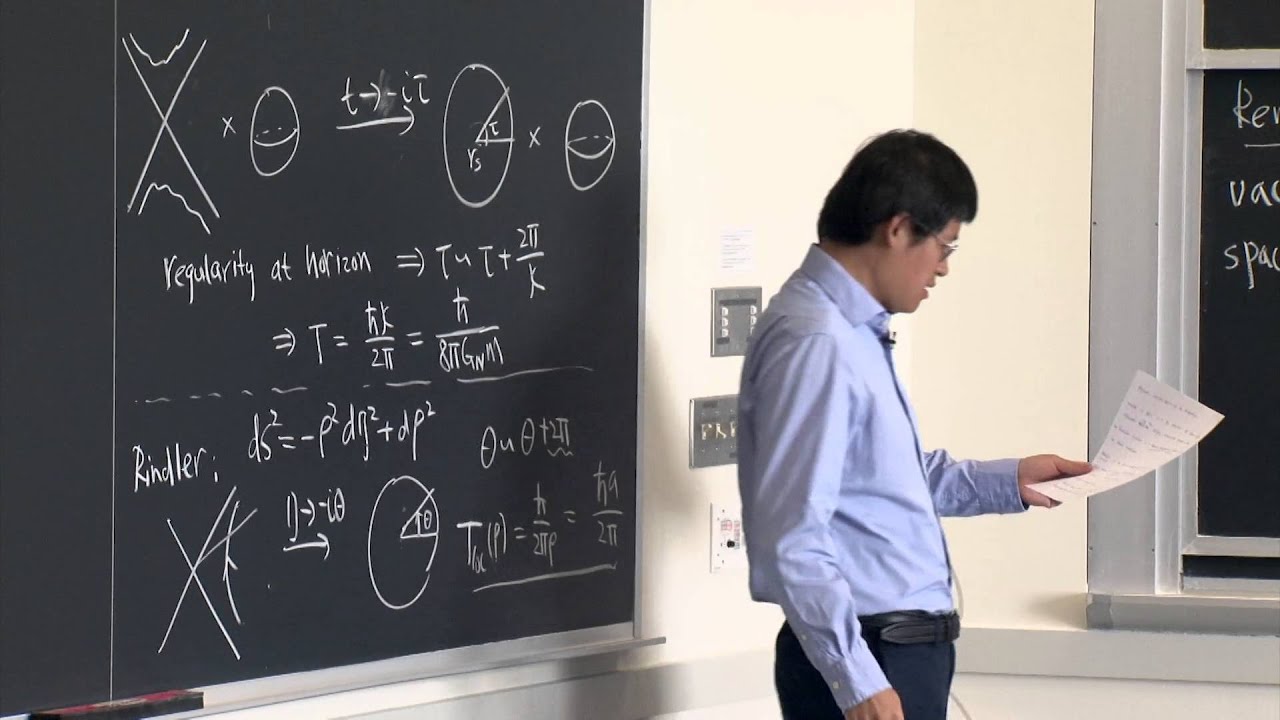


The best introductory lecture about BH, Euclidean space/vacuum, Mikowsky space, Hilbert space,Schwarzschild vacuum, H-H vacuum, Rindler vacuum etc. However, QFT shows and proves that this vacuum is not empty, but filled with fermionic and bosonic fields of virtual particles and who knows what else, that even loan energy (up to 80 Gev) during proton-neutron transformation, to be repaid back in a finite time, implying this field includes energy (virtual or real). What is the space inside the BH containing the Einstein singularity, is it the QF free Euclidean space or Minkowsky or Rindler, enabling Hawking pair of electron-positron formed from the QF at the event horizon, indicating the BH is positively charged, what happens to the positron thus ejected and what information is carried out by Hawking radiation?
Sean hartnoll seems to indicate that a coating of charged particles around the BH may simulate a motor action in which the coating act as a stator, the BH as a rotor of superconducting (very high current and powerful magnetic field), empowering the BH to spin at almost 0.9 c.
Can any one enlighten me, please?
A really good lecture.
This cleared the questions i had, thank you for uploading
"uh uh uh uh uh uh uh"
at least it's not "ahhhheeettt" from kip thorne